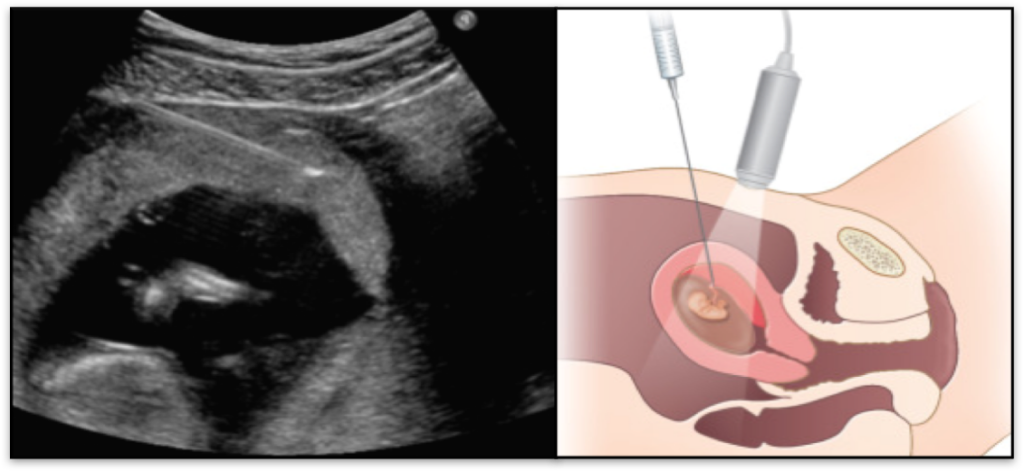
Diagnostic procedures
Chorionic Villus Sampling (CVS)
This test is performed when your pregnancy is between 11 weeks to 14 weeks (ideally after your NT scan) in which a small sample is collected from the placenta which contains fetal cells. This sample is the subjected to definitive tests like FISH, karyotype, microarray, etc. depending upon the indication
Is there any risk associated with this procedure?
There is a documented risk of miscarriage of around 1 in 100 (1%) associated with chorionic villus sampling. However, this risk varies from institution to institution depending upon the expertise of the doctor with some places having a risk of as low as 1 in 500 (0.2%). You can enquire about the centre specific risk for this procedure.
How should I be prepared for this test?
This is an ultrasound guided procedure. It usually takes 2-3 hours for all pre-procedure, procedure proper and post procedure formalities. The procedure proper is only of about 5-10 minutes; however, it may take longer as the scan is highly dependent on the placental position and uterine status. So, it may be wise not to have any other important plans scheduled on the day of your CVS procedure. If you are taking medicines like Aspirin (ecosprin / aspisol) or heparin, the doctor will ask you to stop the medication 1 or 2 days prior to and 2 days after the procedure.
On the day of the test.
You can arrive at the clinic after having a good breakfast or meal. You generally don’t need to have a full urinary bladder for this test, but sometimes the doctor may still ask you to drink water and wait to get the placenta in an optimal position. After completing the formalities and paper work, you will be given a shot of pre-procedure antibiotic. After scanning and deciding the point of entry, the doctor will clean up that area and will give a local anaesthetic in order to make that area numb and insensitive to pain. A thin needle will then be inserted into the placenta and sample taken and stored into a culture media.
What happens after the procedure? Will I have any problems?
You will be advised to rest in the clinic for a couple of hours after the procedure following which you can go home on the same day. You may be then advised to stay at home and rest for 2 days after the procedure following which you may continue with all your routine activities. Some doctors may or may not give you some medicines to have for a few days after the procedure which is completely at the doctor’s discretion and varies according to the institution protocol. It is normal to have some discomfort, mild contractions and pain in the lower abdomen for a couple of days after the procedure. Some women may also have light bleeding or spotting. Persistent contractions and pain or continuous vaginal bleeding or discharge must raise an alarm and one must inform the Doctor about that.
Any special instructions?
Kindly inform the doctor if you are allergic to any medicines in particular, antibiotics. Also, inform the doctor if your blood group is ‘Rh Negative’ (eg. A-ve, B-ve, AB-ve or O-ve) and your partners blood group is ‘Rh Positive’. In such a scenario, you will be administered an injection named ‘Anti D’ just before or after the procedure (within 72 hours) in order to prevent Rh Isoimmunisation (which may cause problem to the baby in current or subsequent pregnancy).
Amniocentesis
This test is performed after your pregnancy is crosses 16 weeks of gestation in which a small sample of amniotic fluid is collected which contains fetal cells. This sample is the subjected to definitive tests like FISH, karyotype, microarray, etc. depending upon the indication
Is there any risk associated with this procedure?
There is a documented risk of miscarriage of around 1 in 100 (1%) associated with amniocentesis. However, this risk varies from institution to institution depending upon the expertise of the doctor with some places having a risk of as less as 1 in 1000 (0.1%). You can enquire about the centre specific risk for this procedure.
Important Note: Both CVS and Amniocentesis are associated with an exactly same risk of miscarriage, ranging from 0.1% to 1% (depending upon the expertise),lower so when performed by highly qualified experts in in Fetal Medicine.
How should I be prepared for this test?
This is an ultrasound guided procedure. It usually takes 2-3 hours for all pre-procedure, procedure proper and post procedure formalities. The procedure proper is only of about 5-10 minutes. It may be wise not to have any other important plans scheduled on the day of your amniocentesis procedure. If you are taking medicines like Aspirin (ecosprin / aspisol) or heparin, the doctor will ask you to stop the medication 1 or 2 days prior to and 2 days after the procedure.
On the day of the test.
You can arrive at the clinic after having a good breakfast or meal. After completing the formalities and paper work and obtaining your sign on a written informed consent, you will be given a shot of pre-procedure I.V. antibiotic. After scanning and deciding the point of entry, the doctor will clean up that area and a thin needle will then be inserted into the amniotic fluid and sample will be collected into an empty tube.
What happens after the procedure? Will I have any problems?
You will be advised to rest in the clinic for a couple of hours after the procedure following which you can go home on the same day. You may be then advised to stay at home and rest for 2 days after the procedure following which you may continue with all your routine activities. Some doctors may or may not give you some medicines to have for a few days after the procedure (which is completely at the doctor’s discretion and varies according to the institution protocol). It is normal to have some discomfort, mild contractions and pain in the lower abdomen for a couple of days after the procedure. Some women may also have light bleeding or spotting. Persistent contractions and pain or continuous vaginal bleeding or discharge must raise an alarm and one must inform the Doctor about that.
Any special instructions?
Kindly inform the doctor beforehand if you are allergic to any medicines in particular, antibiotics. Also, inform the doctor if your blood group is ‘Rh Negative’ (eg. A-ve, B-ve, AB-ve or O-ve) and your partners blood group is ‘Rh Positive’. In such a scenario, you will be administered an injection named ‘Anti D’ after the procedure (within 72 hours) in order to prevent Rh Isoimmunisation (which may cause problem to the baby in current or subsequent pregnancy).
- What if an abnormality is detected? Is there any treatment for chromosomal aneuploidies?
Unfortunately, at present there is no treatment available for chromosomal aneuploidies. You can discuss the options with your doctor and with your family members before arriving to any conclusion. Sometimes, the results may reveal some additional incidental findings which we were primarily not looking for. In such a case, you may require an opinion of a geneticist or a genetic counsellor.
Therapeutic procedures
Fetal Reduction
Sometimes, one may have more than one baby inside the womb. This is called as “multiple pregnancy” or a “multifetal pregnancy”. It can be two babies (twins), three (triplets), four (quadruplets), five (quintuplets) or even more. Such types of pregnancies are more common with artificial reproductive techniques like ovulation induction, IVF, etc. Fetal reduction is a procedure to reduce the number of babies inside the womb to a desirable number. For example, from triplets to twins or singleton. This procedure may also be indicated when one baby out of the two may have a non-correctable problem and which may be harmful for the other baby or the pregnancy as a whole.
What is the advantage of fetal reduction?
Fetal reduction increases the duration of the gestation hence avoiding preterm deliveries and prematurity related morbidities and mortalities.
When is fetal reduction performed?
Fetal reduction is generally performed in the first trimester after a thorough evaluation of all the babies by a detailed NT scan. The chorionicity (type of twinning i.e identical or un-identical) is accurately determined during this scan as the method for reduction may differ based on the chorionicity.
Which baby will be reduced?
After detailed fetal evaluation, if any baby is found to have a serious abnormality or found to be at risk of a problem in future, that baby may be selectively reduced. If all the babies are normal, then the baby which is technically easy to access is selected for reduction.
Is there any risk associated with this procedure?
There is a documented risk of miscarriage of around 2-15% associated with fetal reduction depending upon the number of babies reduced. However, this risk significantly varies from institution to institution depending upon the expertise of the doctor.
How should I be prepared for this test?
This is an ultrasound guided procedure. It usually takes 2-3 hours for all pre-procedure, procedure proper and post procedure formalities. The procedure proper is only of about 10-15 minutes. It is wise not to have any other important plans scheduled on the day of your procedure. If you are taking medicines like Aspirin (ecosprin / aspisol) or heparin, the doctor will ask you to stop the medication 1 or 2 days prior to and 2 days after the procedure.
On the day of the test.
You can arrive at the clinic after having a good breakfast or meal. You generally don’t need to have a full urinary bladder for this scan, but sometimes the doctor may still ask you to drink water and wait. After completing the formalities and paper work and obtaining your sign on a written informed consent, you will be given a shot of pre-procedure I.V. antibiotic. After scanning, selecting the baby and deciding the point of entry, the doctor will clean up that area. A local anaesthetic will then be administered and under constant visualisation of ultrasound, a thin needle will then be inserted into baby and an injection will be administered to instantly stop the heartbeat.
What happens after the procedure? Will I have any problems?
You will be advised to rest in the clinic for sometime after the procedure following which you can go home on the same day. You may be then advised to stay at home and rest for 2 days after the procedure following which you may continue with all your routine activities. Some doctors may or may not give you some medicines to have for a few days after the procedure (which is completely at the doctor’s discretion and varies according to the institution protocol). It is normal to have some discomfort, mild contractions and pain in the lower abdomen for a couple of days after the procedure. Some women may also have light bleeding or spotting. Persistent contractions and pain or continuous vaginal bleeding or discharge must raise an alarm and one must inform the Doctor about that.
Any special instructions?
Kindly inform the doctor beforehand if you are allergic to any medicines in particular, antibiotics. Also, inform the doctor if your blood group is ‘Rh Negative’ (eg. A-ve, B-ve, AB-ve or O-ve) and your partners blood group is ‘Rh Positive’. In such a scenario, you will be administered an injection named ‘Anti D’ after the procedure (within 72 hours) in order to prevent Rh Isoimmunisation (which may cause problem to the baby in current or subsequent pregnancy).
Intrauterine blood transfusion (IUT)
Sometimes, babies may become anaemic while inside the womb. That means the red blood cells in the baby reduce thus decreasing the oxygen carrying capacity of the blood. In such situation, the baby must be given additional red blood cells from outside in order to replenish the fetal reserves.
What are the indications of IUT?
The baby may develop anaemia due to several reasons. The most common is when the mother’s blood group is Rh Negative and the father’s blood group is Rh Positive. In such situation, if the baby’s blood group is Rh Positive, the mother’s antibodies may destroy the baby’s red blood cells. This is called as Rh Incompatibility.
Other causes of fetal anaemia are fetal infections, complications of MCDA twins, fetal or placental tumors, etc.
When is IUT performed?
IUT must be performed as soon as the baby is found to be anaemic. Screening for fetal anaemia is performed in high risk pregnancies by assessing the blood flow inside the baby’s brain. If transfusion is not done in time, this may lead to worsening of fetal anaemia leading to swelling in then baby (hydrops) because of fetal heart failure followed by fetal death. Hence, timely diagnosis and management is lifesaving as fetal anaemia is almost completely treatable while the baby is still inside the womb.
Is there any risk associated with this procedure?
Like all other invasive procedures, even this procedure is associated with a small risk of preterm delivery.
How should I be prepared for this test?
This is an ultrasound guided procedure. It usually takes 2-3 hours for all pre-procedure, procedure proper and post procedure formalities. The procedure proper is of about 30 minutes. It is wise not to have any other important plans scheduled on the day of your procedure. If you are taking medicines like Aspirin (ecosprin / aspisol) or heparin, the doctor will ask you to stop the medication 1 or 2 days prior to and 2 days after the procedure.
On the day of the test.
You can arrive at the clinic after having a good breakfast or meal. After completing the formalities and paper work and obtaining your sign on a written informed consent, you will be given a shot of pre-procedure I.V. antibiotic. After scanning, selecting the point of entry, the doctor will clean up that area. A local anaesthetic will then be administered and under constant visualisation of ultrasound, a thin needle will then be inserted into the umbilical cord or intraabdominal portion of umbilical vein and blood will be transfused into the baby.
The blood which is used for transfusion is O negative blood which has been specially treated and tested for certain parameters.
What happens after the procedure? Will I have any problems?
You will be advised to rest in the clinic for a couple of hours after the procedure following which you can go home on the same day. You may be then advised to stay at home and rest for 3-4 days after the procedure following which you may continue with all your routine activities. Some doctors may or may not give you some medicines to have for a few days after the procedure (which is completely at the doctor’s discretion and varies according to the institution protocol). It is normal to have some discomfort, mild contractions and pain in the lower abdomen for a couple of days after the procedure. Some women may also have light bleeding or spotting. Persistent contractions and pain or continuous vaginal bleeding or discharge must raise an alarm and one must inform the Doctor about that.
Will the procedure be repeated again?
Sometimes, especially when performed earlier in gestation, the baby may again become anaemic within a few weeks after the procedure. In such situations, if the baby is not ready to be delivered, the procedure must be repeated so on and so forth till the baby is completely matured and ready to come out.
Fetoscopic laser ablation (FLA) in TTTS
It is a therapeutic procedure performed to treat a complication known as Twin to Twin Transfusion Syndrome (TTTS). It’s is a complication specific to monochorionic (MCDA) twin or Identical twin pregnancy. In such pregnancies, both babies acquire nutrition and blood supply from a single placenta. Complications may arise because of unequal sharing of placenta owing to disproportionate vascular communications between the two babies. Through such communications, blood is transferred from one twin (donor twin) to the other twin (recipient twin) thus adversely affecting both the babies.TTTS may affect 20% of MCDA pregnancies. In FLA these problem causing communicating vessels or anastomoses are blocked using laser energy.
What are the indications of FLA?
TTTS and some cases of selective fetal growth restriction are the indications of FLA.
When is FLA performed?
TTTS generally sets in after 16 weeks of gestation. The severity may vary depending upon the number of vascular anastomoses. FLA is performed depending upon the severity and progression of this condition.
What happens if a pregnancy is complicated with TTTS?
In milder forms, the condition may be self-limiting and may not have much adverse effects on the pregnancy. However, when progressive and severe, it may have adverse effects. If not treated, almost all such cases lead to intrauterine fetal demise of both babies. If FLA is performed at the right time, in 1/3rd of the cases, both twins will survive, in 1/3rd of cases one of the baby survive and in the remaining 1/3rd, none of the babies will survive.
Is there any risk associated with this procedure?
Like all other invasive procedures, even this procedure is associated with a risk of preterm delivery.
How should I be prepared for this test?
This is a fetoscopic procedure. It usually takes 2-3 days for all pre-procedure, procedure proper and post procedure care. The procedure proper is of about 2-3 hours.
You will be admitted in the hospital a day prior to the procedure and will undergo certain investigations and clearances. The procedure may be performed under local or spinal anaesthesia in an operation theatre. Post procedure, you will be kept under observation for a day and discharged on the next day. Further follow up scans will be done as recommended.
Other therapeutic procedures
Other therapeutic procedures like laser ablations for chorioangioma and shunt placement for various conditions like Pleural effusion or hydrothorax, Congenital Pulmonary Airway Malformation (CPAM) and Bladder outlet obstruction are also performed.